The milk production impacts of liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) infection in dairy cows
Certainl1. Introduction to Contagious Ecthyma (Orf Disease) 2. Causes and Transmission of Orf Virus 3. Symptoms of Orf Disease in Goats and Sheep 4. Diagnosis and Detection Methods 5. Current Global and Regional Status of Orf Disease 6. Recent Outbreaks and Research Updates 7. Treatment and Supportive Care for Infected Animals 8. Prevention and Control Strategies 9. The Role of Vaccination in Orf Management 10. Zoonotic Potential: Orf Transmission to Humans 11. Economic Impact on Sheep and Goat Farming 12. Best Farm Practices to Reduce Disease Spread 13. Conclusion: Staying Ahead of Orf in Your Herd y! Here are some **subtitles** you can use for your blog post about the **milk production impacts of liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) infection in dairy cows** — ready for copy-paste: --- **Subtitles for Blog Post:** * *Understanding the Hidden Cost of Liver Fluke in Dairy Herds* * *How Fasciola hepatica Infection Reduces Milk Yield* * *The Economic Toll of Parasites in Dairy Farming* * *Why Parasite Control Matters for Milk Production* * *Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management of Liver Fluke in Cows* * *From Infected to Inefficient: The Dairy Cow’s Silent Struggle* * *Liver Fluke Infections and Their Impact on Herd Performance* * *Preventing Production Losses Through Effective Fluke Management* * *The Role of Veterinary Intervention in Controlling Fascioliasis* * *Improving Milk Output Through Parasite Prevention Strategies* --- Let me know if you want the blog structured with these subtitles or if you need a full article outline!

Highlights
- Infection status was determined using serum antibody analysis.
- In spring 48 % and autumn 38 % of cows were categorised Fasciola hepatica antibody negative.
- In spring 34 % and autumn 48 % of cows were categorised Fasciola hepatica antibody strong positive.
- Cows negative in spring and strong positive in autumn had a 0.24 % point decrease in milk fat percentage.
- The economic cost was calculated at NZD 60.2 per cow.
Abstract
The impact of fasciolosis has been estimated on many occasions and can vary from mild to severe effects on animal productivity. The aim of the current study was to utilise observations on seroconversion of dairy cattle to Fasciola hepatica over the course of a lactation and compare their milk production with other cattle who remained serologically negative throughout the same lactation. Four spring-calving dairy herds on the West Coast of the South Island of New Zealand were selected based on prior knowledge of endemic liver fluke infection. Over the four herds, a total of 485 cows were blood sampled twice during one lactation, in early November (spring) and early March (autumn). The F. hepatica antibody titre of F. hepatica antibody was quantified using a commercial ELISA test (IDEXX Fasciolosis Verification, IDEXX Europe BV, Hoofdorp, The Netherlands). Milk production was estimated by a series of 3–4 herd tests over the lactation where each cow is individually measured during the morning and evening milking on the same day with samples analysed for milk yield, milk fat (MF), protein (MP), lactose (ML) and total milk solids (MS). Energy corrected milk (ECM) was then calculated using the formula: ECM (kg/d) = 12.55 × MF (kg/d) + 7.39 × MP (kg/d) + 0.2595 × milk yield (kg/d). At the spring sampling, 52 % of cows had antibodies detected which increased to 63 % in autumn. For the sampled cows, those that were in the negative IDEXX test category in autumn and spring were categorised as ‘uninfected’ while those which were negative in spring and seroconverted to the strong positive category in autumn were categorised as ‘infected’.
Keywords
Fasciola hepatica
Dairy herds
West Coast New Zealand
IDEXX Fasciolosis verification ELISA test
Introduction
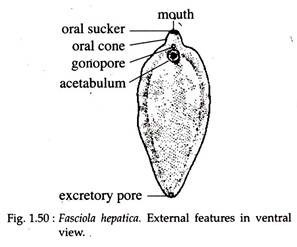
Fasciola hepatica, commonly known as the liver fluke, is a parasitic flatworm that primarily affects the liver of various animals, including goats, sheep, and cattle. It causes a disease known as fascioliasis, which can result in significant economic losses in livestock production. The parasite’s life cycle involves a freshwater snail as an intermediate host, making wet, marshy grazing areas high-risk zones for infection. Goats become infected by ingesting contaminated water or forage that carries the encysted larval stage called metacercariae. Once inside the goat, the larvae migrate through the intestinal wall, travel to the liver, and eventually settle in the bile ducts. There, they mature into adult flukes, feeding on liver tissue and blood. This causes liver damage, inflammation, and can lead to anemia, weight loss, reduced productivity, and in severe cases, death.
Clinical signs include
lethargy, poor appetite, diarrhea, and bottle jaw (fluid accumulation under the jaw due to low protein levels) and severe anemia. Diagnosis is typically done by fecal examination for fluke eggs or liver examination during necropsy. Control strategies involve regular deworming with effective flukicides like triclabendazole, avoiding grazing in snail-infested areas, and improving pasture drainage. Proper herd management and monitoring programs are essential to reduce the risk of infection. Fascioliasis is also a zoonotic disease, meaning it can infect humans, usually through eating contaminated water plants or drinking unsafe water. Therefore, both animal health and public health considerations make liver fluke control a priority in livestock farming.

Milk production (litres or kilograms) losses due to the presence of liver fluke infection or improved production after treatment have been reported as 3–15 % in Europe 16–32 % in the central Americas ). Impacts on the milk constituents (MF, ML, MP) of 0.06 kg/cow/day or 0.06–2.2 % have also been reported. To develop a model to predict the impact of liver fluke infection on cows in Switzerland,determined that infected herds had a 10 % reduction in milk yield (litres/cow/day). Not all studies, however, have been able to determine a statistically significant impact on milk production with impacts at the cow level not always being evident at the herd level. These effects may be lost due to too few cows in the herd having a production limiting infection, even though the prevalence was high.
The impact of liver fluke infection on milk production have either measured the impact of active infection against no infection, or flukicide treatment against no treatment in infected animals, at the individual and herd level. These studies are often conducted in herds which calve all year round, with individual cows entering and leaving the herd throughout the year and are thus at different stages of lactation when the trials are conducted. For example, the milk volume, fat and protein composition of milk changes markedly over the lactation period which makes measuring the effect of infection or treatment difficult to estimate and since cows will be at different stages of lactation at the time of testing, the impact of liver fluke infection on these parameters, although apparent at the individual cow level may be masked at the herd level. This situation is different in New Zealand, where all cows are at a similar stage in lactation due to seasonal spring calving with a greater likelihood that changes at the cow level will also be apparent at the herd level.

The aim of this longitudinal study was to serum sample dairy cows, preferentially selecting those in the first or second lactation, from four herds on two occasions during their lactation, once in November (spring) and again in March (autumn) to investigate the associations between the change of anti-fasciola antibody titre at those two time points with milk production parameters, with the economic cost of any production loss estimated.
Materials and methods
2.1. Animal selection and sampling schedule
This was a longitudinal study of the impact on milk production of liver fluke infection of dairy cows from four herds from the West Coast region of the South Island, New Zealand (Latitude −41.369 to −42.690 degrees South, Longitude 172.096 to 171.036 degrees East) between November 2018 (spring) and March 2019 (autumn). The herds used in this study were spring calving dairy cows that supplied milk to Westland Milk Products (WMP), Hokitika, New Zealand, formerly known as Westland Milk Cooperative. These herds were selected based on having a history of endemic liver fluke infection identified by bulk milk ELISA and the farmer’s willingness to be part of the study.
Cow breed categorisation
Cow breeds were classified according to the farmers records as either cross-bred (may have a combination of Jersey, Friesian, Ayrshire or other genetics), Jersey cross (predominantly Jersey but not purebred), Jersey, Friesian cross (predominantly Friesian but not purebred) or Friesian. No attempt was made to determine how each farmer classified the breed of the cows in their herd.
2.3. Serum sampling
At both visits cattle were blood sampled from the coccygeal vein. Samples were transferred to an insulated carrier containing frozen pads to be sent to the laboratory on overnight courier on the day of sampling or stored chilled and transported by car to Massey University on the following day. On arrival at the laboratory the blood samples were centrifuged at 1100 rpm for 15 min (Thermo Scientific, Heraeus Megafuge 40) and the serum was pipetted into labelled 1.5 mL Eppendorf tubes. Paired samples of serum from each animal were stored at −20 °C.
Serum ELISA testing
The F. hepatica specific f2 antigen antibody titre, in the serum samples was quantified using a commercial ELISA test (IDEXX Fasciolosis Verification, IDEXX Europe BV, Hoofdorp, The Netherlands) including positive control (PC) and negative control (NC) samples as per kit instructions. Both the autumn and spring serum samples were thawed and analysed by the same technician 21–27 months after sampling.
Milk production data
Farmers were requested to provide access to their herd performance recording data (herd test) collected up to four times for the current lactation, carried out by trained technicians. For this procedure, milk was collected at both a morning and afternoon milking at each sample point and analysed for volume (L), milk fat, protein and lactose (percentage (%) and weight (kg)), milk solids (kg) and somatic cell count. Data was categorised by farm identifier, cow identification number, number of the herd test for that lactation (one to four) and date of the herd test, cow breed, cow age (years), lactation number (1,2, 3+), IDEXX serum SP% and category and the milk production data from the herd test results.
Calculating the economic impact of liver fluke infection on milk production
In the 2017/18 lactation the average herd supplying Westland Milk had 415 cows and produced 4150 L of milk per cow (wwwvetrinaryhub.info). The values of NZD 6.75/kg for milk solids, comprising milk protein at 7.6506/kg NZD and milk fat at NZD 6.044/kg were used in calculations of the economic cost of infection. These values were those to dairy farmers in New Zealand during 2022/23.
Statistics
A model of the lactational change in milk production parameters was developed, describing the lactation curve for each milk components. The data structure itself was hierarchical and had 3 levels of information and potential variability, the 1st level was the repeated herd tests on individual cows, the 2nd level was the individual cows, and the 3rd level was the herds from which the individual cows were selected
Separate statistical models with the following milk production parameters, ECM, milk solids (MS), milk fat % (MF%), milk protein % (MP%), milk lactose % (ML%) as the outcome variable were first created for all cows from all herds using a repeated measures random effects model in R using packages . The variable days in milk (DIM) was calculated as the number of days from calving to the date of each herd test.
Results
3.1. Cow sampling and herd testing
A total of 485 cows were blood sampled from November 12 to 15, 2018 (Spring), and again from March 6–10, 2019 (Autumn), with corresponding herd test data. A total of 1694 complete cow data points were analysed, ranging from 102 to 153 (17–26 %) cows from each of the four herds. Using calving dates provided by farmers, the average (and range) of days in milk (DIM) at Spring sampling was 83 (37–160) and Autumn 197 (151–274). Herds B and H performed three herd tests while herds A and I performed four. Of the 485 cows, 266 were first lactation, 125 second and 94 third or more lactation.
Table 1: Dates of herd tests, blood sampling and the number of paired serum samples for each herd.
| Herd | Blood sampling dates | Herd test dates | Number of cows with paired samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 12/11/2018 | 06/03/2019 | 30/09/2018 | 11/12/2018 | 12/02/2019 | 19/04/2019 | 126 |
| B | 13/11/2018 | 08/03/2019 | 19/12/2018 | 03/03/2019 | 02/05/2019 | 104 | |
| H | 14/11/2018 | 09/03/2019 | 27/09/2018 | 05/12/2019 | 04/02/2019 | 101 | |
| I | 15/11/2018 | 10/03/2019 | 24/09/2018 | 22/11/2018 | 21/01/2019 | 16/04/2019 | 155 |
IDEXX category change
Between the Spring and Autumn sampling points there was a decrease in the percentage of cows in the negative, mild positive and positive categories with an increase in the strong positive category. The percentage of cows in each diagnostic category was skewed toward either negative or strong positive at both sampling points
Calculating the economic cost of liver fluke infection on milk production
A 0.24 %-point reduction in MF in an ‘infected’ cow equates to 2.4 g MF/L lower production compared to an ‘uninfected’ cow. With MF valued at NZD 6.044/kg and the average herd producing 4150 l of milk per cow, this is a loss of NZD 60.2 per cow. In this study 50/235 (21 %) cows were ‘uninfected’ at the first sampling and ‘infected’ at the second. If this were representative of the average West Coast herd of 415 cows, the economic cost would be NZD 5246.3 per herd.





hs8h1q